CIT Bank custodial accounts: They sound boring, right? Wrong. This isn’t your grandpa’s savings account. We’re diving deep into the world of CIT Bank’s custodial offerings, exploring everything from UTMA/UGMA implications to the nitty-gritty of online account management. Think of it as a financial adventure, minus the questionable pyramid schemes.
We’ll unravel the complexities, compare fees, and even toss in a few hypothetical scenarios to keep things interesting. Buckle up, buttercup.
This guide dissects CIT Bank’s custodial account options, walking you through the setup, investment strategies, legal aspects, and security measures. We’ll cover different account types, eligibility requirements, and the best practices for protecting your assets. Whether you’re setting up a fund for a minor or managing a more complex portfolio, this deep dive will equip you with the knowledge you need to navigate the world of CIT Bank custodial accounts with confidence – and maybe even a little excitement.
Understanding CIT Bank Custodial Accounts
CIT Bank offers various custodial accounts designed to manage assets for minors or other beneficiaries. Understanding the nuances of each account type, including eligibility, fees, and services, is crucial for selecting the right option. This section details the different account types, their requirements, and a comparison of their features.
CIT Bank Custodial Account Types
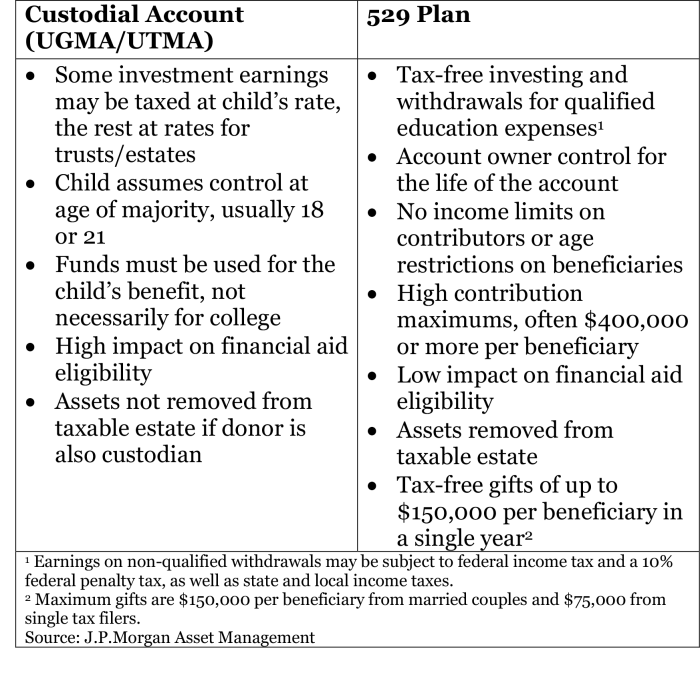
CIT Bank provides several custodial account types, each tailored to specific needs and circumstances. These may include, but are not limited to, accounts for minors under the Uniform Transfers to Minors Act (UTMA) or Uniform Gifts to Minors Act (UGMA), and potentially other types depending on the specific needs of the beneficiary and the custodian.
Eligibility Requirements for CIT Bank Custodial Accounts
Eligibility criteria vary depending on the specific account type. Generally, a custodian (the adult managing the account) must meet certain age and residency requirements. Minors, as beneficiaries, typically require proof of identity and relationship to the custodian. Specific documentation requirements are Artikeld during the account application process.
Fee and Service Comparison of CIT Bank Custodial Accounts
Fees and services associated with CIT Bank custodial accounts vary based on account type and activity levels. Some accounts might have minimum balance requirements or charge fees for specific transactions. A detailed fee schedule is typically available on the CIT Bank website or through a customer service representative.
Comparison of CIT Bank Custodial Account Features
The following table summarizes key features of different CIT Bank custodial account types. Note that this is a simplified representation, and actual features may vary.
| Account Type | Minimum Deposit | Annual Fee | Account Access Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| UTMA/UGMA Account | $0 (May vary depending on specific offering) | $0 (May vary depending on specific offering) | Online, Phone, Mail |
| [Other Account Type 1 – if applicable] | [Minimum Deposit] | [Annual Fee] | [Account Access Methods] |
| [Other Account Type 2 – if applicable] | [Minimum Deposit] | [Annual Fee] | [Account Access Methods] |
Account Setup and Management
Opening and managing a CIT Bank custodial account involves several straightforward steps. Understanding these processes ensures efficient account management and access to the account’s features and benefits.
Opening a CIT Bank Custodial Account
The process typically begins with an online application or by contacting CIT Bank customer service. Applicants will need to provide personal information for both the custodian and the beneficiary, along with supporting documentation.
Required Documentation for Account Opening
Necessary documentation usually includes government-issued identification for the custodian and beneficiary, proof of address, and potentially additional documents depending on the account type and the beneficiary’s age. Specific requirements are detailed on the CIT Bank application form.
Managing the Account Online and via Phone
CIT Bank offers online account management through their website, allowing for convenient access to account balances, transaction history, and other account information. Phone support is also available for assistance with account management and inquiries.
Adding Beneficiaries to a Custodial Account
Adding beneficiaries to an existing custodial account usually requires submitting a written request to CIT Bank, along with the necessary documentation for the new beneficiary. The process may involve completing a beneficiary addition form and providing supporting identification and relationship documentation.
- Submit a written request to CIT Bank.
- Complete the beneficiary addition form.
- Provide necessary documentation for the new beneficiary.
- Await confirmation from CIT Bank.
Investment Options and Strategies within a CIT Bank Custodial Account
Source: squarespace-cdn.com
Custodial accounts at CIT Bank offer a range of investment options to help grow the assets for the beneficiary. Understanding the available options and potential tax implications is crucial for effective financial planning.
Investment Options Available
Investment options may include various securities such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs). The specific options available may depend on the account type and the custodian’s investment preferences.
CIT Bank’s custodial account services cater to a specific clientele requiring secure asset management. However, the availability of more general-purpose accounts, such as checking accounts, is a separate consideration; to determine whether CIT Bank offers checking accounts, refer to this resource: does cit bank have checking accounts. Understanding this distinction is crucial when evaluating CIT Bank’s overall suitability for individual banking needs, separate from its custodial account offerings.
Types of Securities That Can Be Held
CIT Bank custodial accounts typically allow for a diverse range of securities, providing flexibility in investment strategies. This may include stocks listed on major exchanges, bonds issued by governments or corporations, and various mutual funds and ETFs.
Tax Implications of Different Investment Strategies
The tax implications of investment strategies within a custodial account depend on factors such as the type of investments, the account’s growth, and applicable tax laws. It is advisable to consult with a tax professional for personalized guidance.
Potential Investment Strategies for Different Risk Tolerances
Investment strategies should align with the beneficiary’s long-term financial goals and risk tolerance. A conservative approach might focus on low-risk investments like bonds, while a more aggressive approach might incorporate higher-risk, higher-potential-return investments such as stocks.
- Conservative: Primarily bonds and low-risk mutual funds.
- Moderate: A mix of bonds, stocks, and mutual funds.
- Aggressive: Primarily stocks and higher-risk investments.
Legal and Regulatory Aspects
Custodial accounts are subject to specific legal and regulatory frameworks. Understanding these aspects is crucial for both the custodian and the beneficiary.
Legal Responsibilities of the Custodian and Account Owner
The custodian has a fiduciary responsibility to manage the account assets in the best interest of the beneficiary. This includes making prudent investment decisions and maintaining accurate records.
Implications of UTMA/UGMA
UTMA/UGMA accounts offer significant tax advantages and simplify the transfer of assets to minors. Understanding the implications of these acts, including the age of majority and tax reporting, is essential.
Regulatory Framework Governing Custodial Accounts
Custodial accounts are subject to various regulations, including those related to securities laws, banking regulations, and tax laws. These regulations ensure the protection of assets and the transparency of account operations.
Reporting Requirements for Custodial Accounts
Custodians are typically required to file annual tax returns reporting the income generated within the custodial account. The specific reporting requirements depend on the account’s income and applicable tax laws.
Security and Risk Management
Protecting the assets within a custodial account is paramount. CIT Bank employs various security measures, but understanding potential risks and mitigation strategies is crucial for account holders.
Security Measures Employed by CIT Bank
CIT Bank utilizes various security measures, including encryption, fraud detection systems, and multi-factor authentication, to protect custodial accounts from unauthorized access and fraud.
Risks Associated with Holding Assets in a Custodial Account
Potential risks include market fluctuations impacting investment values, the risk of fraud, and the potential for errors in account management. Diversification and regular monitoring can help mitigate these risks.
Mitigating Risks Associated with Online Access and Fraud
Strong passwords, regular password changes, and awareness of phishing scams are essential for mitigating online access risks. Monitoring account activity regularly can help detect and prevent fraudulent activity.
Best Practices for Securing a CIT Bank Custodial Account
- Use strong, unique passwords.
- Enable multi-factor authentication.
- Regularly monitor account activity.
- Be wary of phishing scams and suspicious emails.
- Report any suspicious activity immediately to CIT Bank.
Account Closure and Transfer
Closing or transferring a CIT Bank custodial account involves specific procedures. Understanding these steps ensures a smooth and efficient process.
Closing a CIT Bank Custodial Account
Closing a custodial account typically involves submitting a written request to CIT Bank, along with any required documentation. The process may involve transferring the assets to another account or distributing them to the beneficiary.
Transferring Assets to Another Institution
Transferring assets to another institution usually involves completing a transfer form and providing the necessary account information for the receiving institution. CIT Bank will facilitate the transfer according to their procedures.
Checklist for Closing and Transferring Assets
- Submit a written request to CIT Bank.
- Complete the necessary transfer forms.
- Provide account information for the receiving institution.
- Confirm the transfer with CIT Bank and the receiving institution.
Potential Fees Associated with Closing or Transferring
CIT Bank may charge fees for closing or transferring a custodial account. These fees, if any, will be Artikeld in the account agreement or communicated during the process.
Illustrative Example: A Minor’s Custodial Account

Source: investise.com
A custodial account can significantly benefit a minor by providing a secure way to manage and grow assets for their future. This section illustrates a hypothetical example.
Example of a Minor’s Custodial Account
Let’s say John, a parent, opens a UTMA account for his 5-year-old daughter, Sarah. He contributes $5,000 initially and invests in a diversified portfolio of low-risk mutual funds. Over the years, the account grows steadily due to both contributions and investment returns. By the time Sarah turns 18, the account balance might have significantly increased, providing a strong foundation for her future education or other endeavors.
Account Setup Process, Documentation, and Beneficiary Information
John provides his and Sarah’s identification documents, proof of address, and completes the necessary paperwork for the UTMA account opening. He designates himself as the custodian and Sarah as the beneficiary.
Investment Choices and Strategies Suitable for a Minor’s Account
Given Sarah’s age and long-term financial goals, John opts for a conservative investment strategy focusing on low-risk, diversified mutual funds to ensure steady growth with minimal risk of significant losses.
Hypothetical Scenario Illustrating Account Growth

Source: time.com
Assuming an average annual return of 5%, with regular contributions of $1,000 per year, the account could grow to approximately $20,000 by the time Sarah turns 18. This is a simplified example and actual returns may vary.
Epilogue
So, there you have it – a comprehensive look at CIT Bank custodial accounts. From the initial setup to the eventual closure, we’ve covered the essentials, the nuances, and even a few unexpected twists. Remember, while this guide provides valuable information, consulting a financial advisor is always recommended for personalized advice tailored to your specific circumstances. Now go forth and conquer your financial future (responsibly, of course).